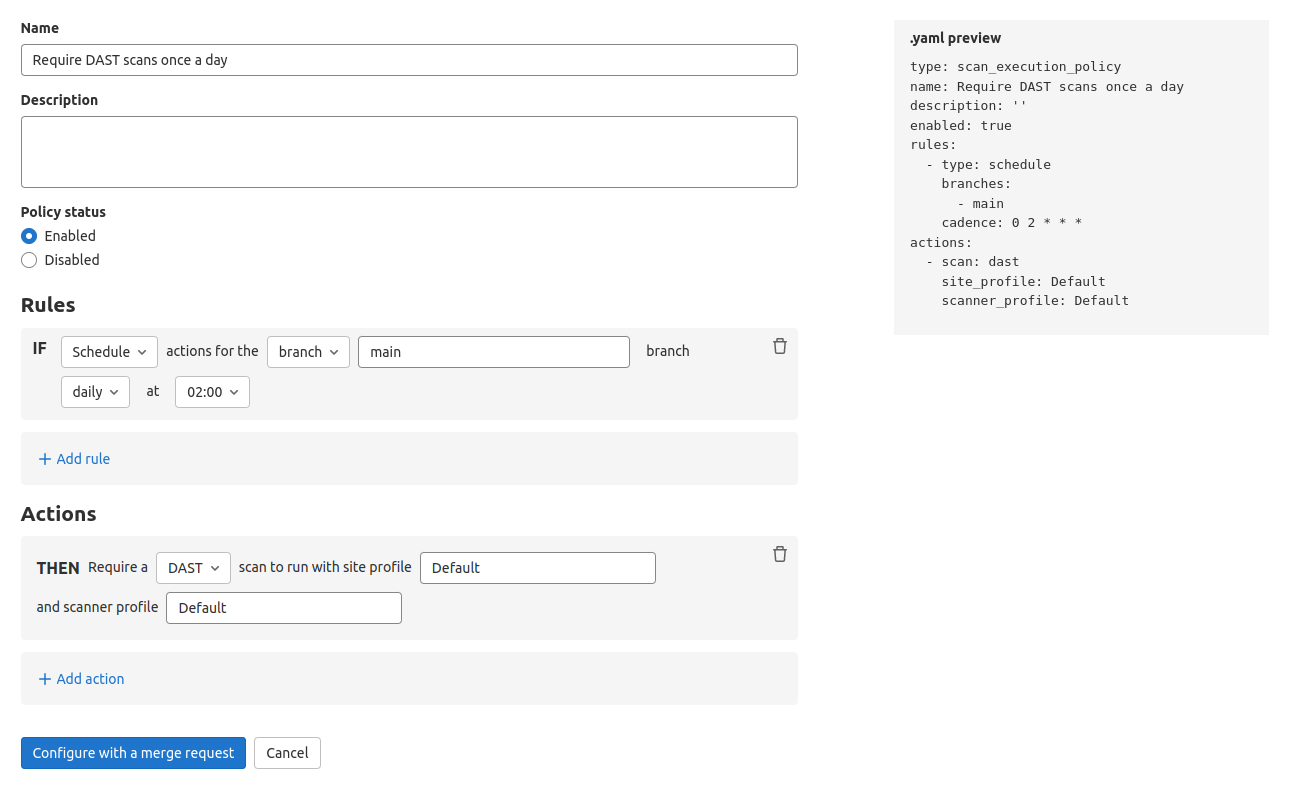
- Scan execution policy editor
- Scan execution policies schema
- Scan execution policy schema
pipelinerule type-
schedulerule type scanaction type- Example security policies project
- Example for scan execution policy editor
- Avoiding duplicate scans
Scan execution policies
- Group-level security policies were introduced in GitLab 15.2.
- Group-level security policies were enabled on GitLab.com in GitLab 15.4.
- Operational container scanning introduced in GitLab 15.5
Group, subgroup, or project owners can use scan execution policies to require that security scans run on a specified schedule or with the project (or multiple projects if the policy is defined at a group or subgroup level) pipeline. Required scans are injected into the CI pipeline as new jobs with a long, random job name. In the unlikely event of a job name collision, the security policy job overwrites any pre-existing job in the pipeline. If a policy is created at the group-level, it applies to every child project or subgroup. A group-level policy cannot be edited from a child project or subgroup.
This feature has some overlap with compliance framework pipelines, as we have not unified the user experience for these two features. For details on the similarities and differences between these features, see Enforce scan execution.
test stage of the pipeline. If you modify the default pipeline
stages,
to remove the test stage, jobs will run in the scan-policies stage instead. This stage is injected into the CI pipeline at evaluation time if it doesn’t exist. If the build stage exists, it is injected just after the build stage. If the build stage does not exist, it is injected at the beginning of the pipeline. DAST scans always run in the dast stage. If this stage does not exist, then a dast stage is injected at the end of the pipeline.Scan execution policy editor
Once your policy is complete, save it by selecting Create via merge request at the bottom of the editor. You are redirected to the merge request on the project’s configured security policy project. If one does not link to your project, a security policy project is automatically created. Existing policies can also be removed from the editor interface by selecting Delete policy at the bottom of the editor.
Most policy changes take effect as soon as the merge request is merged. Any changes that do not go through a merge request and are committed directly to the default branch may require up to 10 minutes before the policy changes take effect.
Scan execution policies schema
The YAML file with scan execution policies consists of an array of objects matching scan execution
policy schema nested under the scan_execution_policy key. You can configure a maximum of 5
policies under the scan_execution_policy key. Any other policies configured after
the first 5 are not applied.
When you save a new policy, GitLab validates its contents against this JSON schema. If you’re not familiar with how to read JSON schemas, the following sections and tables provide an alternative.
| Field | Type | Possible values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
scan_execution_policy
|
array of scan execution policy
| List of scan execution policies (maximum 5) |
Scan execution policy schema
| Field | Type | Possible values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
name
| string
| Name of the policy. Maximum of 255 characters. | |
description (optional)
| string
| Description of the policy. | |
enabled
| boolean
|
true, false
| Flag to enable (true) or disable (false) the policy.
|
rules
|
array of rules
| List of rules that the policy applies. | |
actions
|
array of actions
| List of actions that the policy enforces. |
pipeline rule type
This rule enforces the defined actions whenever the pipeline runs for a selected branch.
| Field | Type | Possible values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
type
| string
| pipeline
| The rule’s type. |
branches
|
array of string
|
* or the branch’s name
| The branch the given policy applies to (supports wildcard). |
schedule rule type
This rule enforces the defined actions and schedules a scan on the provided date/time.
| Field | Type | Possible values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
type
| string
| schedule
| The rule’s type. |
branches
|
array of string
|
* or the branch’s name
| The branch the given policy applies to (supports wildcard). This field is required if the agents field is not set.
|
cadence
| string
| CRON expression (for example, 0 0 * * *)
| A whitespace-separated string containing five fields that represents the scheduled time. |
agents
| object
| The name of the GitLab agents where cluster image scanning runs. The object key is the name of the Kubernetes agent configured for your project in GitLab. This field is required if the branches field is not set.
|
GitLab supports the following types of CRON syntax for the cadence field:
- A daily cadence of once per hour at a specified hour, for example:
0 18 * * * - A weekly cadence of once per week on a specified day and at a specified hour, for example:
0 13 * * 0
agents field, required for Operational Container Scanning, the CRON expression is evaluated in UTC using the system-time of the Kubernetes-agent pod. If not using the agents field, the CRON expression is evaluated in standard UTC time from GitLab.com. If you have a self-managed GitLab instance and have changed the server time zone, the CRON expression is evaluated with the new time zone.
agent schema
Use this schema to define agents objects in the schedule rule type.
| Field | Type | Possible values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
namespaces
|
array of string
| The namespace that is scanned. If empty, all namespaces are scanned. |
Policy example
- name: Enforce Container Scanning in cluster connected through my-gitlab-agent for default and kube-system namespaces
enabled: true
rules:
- type: schedule
cadence: '0 10 * * *'
agents:
<agent-name>:
namespaces:
- 'default'
- 'kube-system'
actions:
- scan: container_scanning
The keys for a schedule rule are:
-
cadence(required): a CRON expression for when the scans are run -
agents:<agent-name>(required): The name of the agent to use for scanning -
agents:<agent-name>:namespaces(optional): The Kubernetes namespaces to scan. If omitted, all namespaces are scanned.
scan action type
This action executes the selected scan with additional parameters when conditions for at least one
rule in the defined policy are met.
| Field | Type | Possible values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
scan
| string
|
dast, secret_detection, sast, container_scanning, dependency_scanning
| The action’s type. |
site_profile
| string
| Name of the selected DAST site profile. | The DAST site profile to execute the DAST scan. This field should only be set if scan type is dast.
|
scanner_profile
|
string or null
| Name of the selected DAST scanner profile. | The DAST scanner profile to execute the DAST scan. This field should only be set if scan type is dast.
|
variables
| object
| A set of CI variables, supplied as an array of key: value pairs, to apply and enforce for the selected scan. The key is the variable name, with its value provided as a string. This parameter supports any variable that the GitLab CI job supports for the specified scan.
| |
tags
|
array of string
| A list of runner tags for the policy. The policy jobs are run by runner with the specified tags. |
Note the following:
- You must create the site profile and scanner profile with selected names for each project that is assigned to the selected Security Policy Project. Otherwise, the policy is not applied and a job with an error message is created instead.
- Once you associate the site profile and scanner profile by name in the policy, it is not possible
to modify or delete them. If you want to modify them, you must first disable the policy by setting
the
activeflag tofalse. - When configuring policies with a scheduled DAST scan, the author of the commit in the security policy project’s repository must have access to the scanner and site profiles. Otherwise, the scan is not scheduled successfully.
- For a secret detection scan, only rules with the default ruleset are supported. Custom rulesets are not supported.
- A secret detection scan runs in
normalmode when executed as part of a pipeline, and inhistoricmode when executed as part of a scheduled scan. - A container scanning scan that is configured for the
pipelinerule type ignores the agent defined in theagentsobject. Theagentsobject is only considered forschedulerule types. An agent with a name provided in theagentsobject must be created and configured for the project.
Example security policies project
You can use this example in a .gitlab/security-policies/policy.yml file stored in a
security policy project:
---
scan_execution_policy:
- name: Enforce DAST in every release pipeline
description: This policy enforces pipeline configuration to have a job with DAST scan for release branches
enabled: true
rules:
- type: pipeline
branches:
- release/*
actions:
- scan: dast
scanner_profile: Scanner Profile A
site_profile: Site Profile B
- name: Enforce DAST and secret detection scans every 10 minutes
description: This policy enforces DAST and secret detection scans to run every 10 minutes
enabled: true
rules:
- type: schedule
branches:
- main
cadence: "*/10 * * * *"
actions:
- scan: dast
scanner_profile: Scanner Profile C
site_profile: Site Profile D
- scan: secret_detection
- name: Enforce Secret Detection and Container Scanning in every default branch pipeline
description: This policy enforces pipeline configuration to have a job with Secret Detection and Container Scanning scans for the default branch
enabled: true
rules:
- type: pipeline
branches:
- main
actions:
- scan: secret_detection
- scan: sast
variables:
SAST_EXCLUDED_ANALYZERS: brakeman
- scan: container_scanning
In this example:
- For every pipeline executed on branches that match the
release/*wildcard (for example, branchrelease/v1.2.1), DAST scans run withScanner Profile AandSite Profile B. - DAST and secret detection scans run every 10 minutes. The DAST scan runs with
Scanner Profile CandSite Profile D. - Secret detection, container scanning, and SAST scans run for every pipeline executed on the
mainbranch. The SAST scan runs with theSAST_EXCLUDED_ANALYZERvariable set to"brakeman".
Example for scan execution policy editor
You can use this example in the YAML mode of the scan execution policy editor. It corresponds to a single object from the previous example.
name: Enforce Secret Detection and Container Scanning in every default branch pipeline
description: This policy enforces pipeline configuration to have a job with Secret Detection and Container Scanning scans for the default branch
enabled: true
rules:
- type: pipeline
branches:
- main
actions:
- scan: secret_detection
- scan: container_scanning
Avoiding duplicate scans
Scan execution policies can cause the same type of scanner to run more than once if developers include scan jobs in the project’s
.gitlab-ci.yml file. This behavior is intentional as scanners can run more than once with different variables and settings. For example, a
developer may want to try running a SAST scan with different variables than the one enforced by the security and compliance team. In
this case, two SAST jobs run in the pipeline, one with the developer’s variables and one with the security and compliance team’s variables.
If you want to avoid running duplicate scans, you can either remove the scans from the project’s .gitlab-ci.yml file or disable your
local jobs by setting SAST_DISABLED: true. Disabling jobs this way does not prevent the security jobs defined by scan execution
policies from running.