- Build and deployment variables
- Database variables
- Job-disabling variables
- Configure application secret variables
- Update application secrets
- Configure replica variables
- Deploy policy for staging and production environments
- Deploy policy for canary environments
- Incremental rollout to production
- Timed incremental rollout to production
CI/CD variables
Use CI/CD variables to set up the Auto DevOps domain, provide a custom Helm chart, or scale your application.
Build and deployment variables
Use these variables to customize and deploy your build.
| CI/CD variable | Description |
|---|---|
ADDITIONAL_HOSTS
| Fully qualified domain names specified as a comma-separated list that are added to the Ingress hosts. |
<ENVIRONMENT>_ADDITIONAL_HOSTS
| For a specific environment, the fully qualified domain names specified as a comma-separated list that are added to the Ingress hosts. This takes precedence over ADDITIONAL_HOSTS.
|
AUTO_BUILD_IMAGE_VERSION
| Customize the image version used for the build job. See list of versions.
|
AUTO_DEPLOY_IMAGE_VERSION
| Customize the image version used for Kubernetes deployment jobs. See list of versions. |
AUTO_DEVOPS_ATOMIC_RELEASE
| As of GitLab 13.0, Auto DevOps uses --atomic for Helm deployments by default. Set this variable to false to disable the use of --atomic
|
AUTO_DEVOPS_BUILD_IMAGE_CNB_ENABLED
| Set to false to use Herokuish instead of Cloud Native Buildpacks with Auto Build. More details.
|
AUTO_DEVOPS_BUILD_IMAGE_CNB_BUILDER
| The builder used when building with Cloud Native Buildpacks. The default builder is heroku/buildpacks:18. More details.
|
AUTO_DEVOPS_BUILD_IMAGE_EXTRA_ARGS
| Extra arguments to be passed to the docker build command. Using quotes doesn’t prevent word splitting. More details.
|
AUTO_DEVOPS_BUILD_IMAGE_FORWARDED_CI_VARIABLES
| A comma-separated list of CI/CD variable names to be forwarded to the build environment (the buildpack builder or docker build).
|
AUTO_DEVOPS_BUILD_IMAGE_CNB_PORT
| In GitLab 15.0 and later, port exposed by the generated Docker image. Set to false to prevent exposing any ports. Defaults to 5000.
|
AUTO_DEVOPS_CHART
| Helm Chart used to deploy your apps. Defaults to the one provided by GitLab. |
AUTO_DEVOPS_CHART_REPOSITORY
| Helm Chart repository used to search for charts. Defaults to https://charts.gitlab.io.
|
AUTO_DEVOPS_CHART_REPOSITORY_NAME
| Used to set the name of the Helm repository. Defaults to gitlab.
|
AUTO_DEVOPS_CHART_REPOSITORY_USERNAME
| Used to set a username to connect to the Helm repository. Defaults to no credentials. Also set AUTO_DEVOPS_CHART_REPOSITORY_PASSWORD.
|
AUTO_DEVOPS_CHART_REPOSITORY_PASSWORD
| Used to set a password to connect to the Helm repository. Defaults to no credentials. Also set AUTO_DEVOPS_CHART_REPOSITORY_USERNAME.
|
AUTO_DEVOPS_CHART_REPOSITORY_PASS_CREDENTIALS
| From GitLab 14.2, set to a non-empty value to enable forwarding of the Helm repository credentials to the chart server when the chart artifacts are on a different host than repository. |
AUTO_DEVOPS_COMMON_NAME
| From GitLab 15.5, set to a valid domain name to customize the common name used for the TLS certificate. Defaults to le-$CI_PROJECT_ID.$KUBE_INGRESS_BASE_DOMAIN. Set to false to not set this alternative host on the Ingress.
|
AUTO_DEVOPS_DEPLOY_DEBUG
| From GitLab 13.1, if this variable is present, Helm outputs debug logs. |
AUTO_DEVOPS_ALLOW_TO_FORCE_DEPLOY_V<N>
| From auto-deploy-image v1.0.0, if this variable is present, a new major version of chart is forcibly deployed. For more information, see Ignore warnings and continue deploying. |
BUILDPACK_URL
| A full Buildpack URL. Must point to a URL supported by Pack or Herokuish. |
CANARY_ENABLED
| Used to define a deploy policy for canary environments. |
BUILDPACK_VOLUMES
| Specify one or more Buildpack volumes to mount. Use a pipe | as list separator.
|
CANARY_PRODUCTION_REPLICAS
| Number of canary replicas to deploy for Canary Deployments in the production environment. Takes precedence over CANARY_REPLICAS. Defaults to 1.
|
CANARY_REPLICAS
| Number of canary replicas to deploy for Canary Deployments. Defaults to 1. |
CI_APPLICATION_REPOSITORY
| The repository of container image being built or deployed, $CI_APPLICATION_REPOSITORY:$CI_APPLICATION_TAG. For more details, read Custom container image.
|
CI_APPLICATION_TAG
| The tag of the container image being built or deployed, $CI_APPLICATION_REPOSITORY:$CI_APPLICATION_TAG. For more details, read Custom container image.
|
DAST_AUTO_DEPLOY_IMAGE_VERSION
| Customize the image version used for DAST deployments on the default branch. Should usually be the same as AUTO_DEPLOY_IMAGE_VERSION. See list of versions.
|
DOCKERFILE_PATH
| From GitLab 13.2, allows overriding the default Dockerfile path for the build stage |
HELM_RELEASE_NAME
| Allows the helm release name to be overridden. Can be used to assign unique release names when deploying multiple projects to a single namespace.
|
HELM_UPGRADE_VALUES_FILE
| Allows the helm upgrade values file to be overridden. Defaults to .gitlab/auto-deploy-values.yaml.
|
HELM_UPGRADE_EXTRA_ARGS
| Allows extra options in helm upgrade commands when deploying the application. Using quotes doesn’t prevent word splitting.
|
INCREMENTAL_ROLLOUT_MODE
| If present, can be used to enable an incremental rollout of your application for the production environment. Set to manual for manual deployment jobs or timed for automatic rollout deployments with a 5 minute delay each one.
|
K8S_SECRET_*
| Any variable prefixed with K8S_SECRET_ is made available by Auto DevOps as environment variables to the deployed application.
|
KUBE_CONTEXT
| From GitLab 14.5, can be used to select a context to use from KUBECONFIG. When KUBE_CONTEXT is blank, the default context in KUBECONFIG (if any) is used. A context must be selected when used with the agent for Kubernetes.
|
KUBE_INGRESS_BASE_DOMAIN
| Can be used to set a domain per cluster. See cluster domains for more information. |
KUBE_NAMESPACE
| The namespace used for deployments. When using certificate-based clusters, this value should not be overwritten directly. |
KUBECONFIG
| The kubeconfig to use for deployments. User-provided values take priority over GitLab-provided values. |
PRODUCTION_REPLICAS
| Number of replicas to deploy in the production environment. Takes precedence over REPLICAS and defaults to 1. For zero downtime upgrades, set to 2 or greater.
|
REPLICAS
| Number of replicas to deploy. Defaults to 1. Change this variable instead of modifying replicaCount.
|
ROLLOUT_RESOURCE_TYPE
| Allows specification of the resource type being deployed when using a custom Helm chart. Default value is deployment.
|
ROLLOUT_STATUS_DISABLED
| Used to disable rollout status check because it does not support all resource types, for example, cronjob.
|
STAGING_ENABLED
| Used to define a deploy policy for staging and production environments. |
TRACE
| Set to any value to make Helm commands produce verbose output. You can use this setting to help diagnose Auto DevOps deployment problems. |
Database variables
true for POSTGRES_ENABLED was deprecated
in GitLab 15.8. In GitLab 16.0, the default value will change to false.Use these variables to integrate CI/CD with PostgreSQL databases.
| CI/CD variable | Description |
|---|---|
DB_INITIALIZE
| Used to specify the command to run to initialize the application’s PostgreSQL database. Runs inside the application pod. |
DB_MIGRATE
| Used to specify the command to run to migrate the application’s PostgreSQL database. Runs inside the application pod. |
POSTGRES_ENABLED
| Whether PostgreSQL is enabled. Defaults to true until GitLab 16.0, when the default will change to false. Set to false to disable the automatic deployment of PostgreSQL.
|
POSTGRES_USER
| The PostgreSQL user. Defaults to user. Set it to use a custom username.
|
POSTGRES_PASSWORD
| The PostgreSQL password. Defaults to testing-password. Set it to use a custom password.
|
POSTGRES_DB
| The PostgreSQL database name. Defaults to the value of $CI_ENVIRONMENT_SLUG. Set it to use a custom database name.
|
POSTGRES_VERSION
| Tag for the postgres Docker image to use. Defaults to 9.6.16 for tests and deployments as of GitLab 13.0 (previously 9.6.2). If AUTO_DEVOPS_POSTGRES_CHANNEL is set to 1, deployments uses the default version 9.6.2.
|
POSTGRES_HELM_UPGRADE_VALUES_FILE
| In GitLab 13.8 and later, and when using auto-deploy-image v2, this variable allows the helm upgrade values file for PostgreSQL to be overridden. Defaults to .gitlab/auto-deploy-postgres-values.yaml.
|
POSTGRES_HELM_UPGRADE_EXTRA_ARGS
| In GitLab 13.8 and later, and when using auto-deploy-image v2, this variable allows extra PostgreSQL options in helm upgrade commands when deploying the application. Using quotes doesn’t prevent word splitting.
|
POSTGRES_CHART_REPOSITORY
| Helm Chart repository used to search for PostgreSQL chart. Defaults to https://raw.githubusercontent.com/bitnami/charts/eb5f9a9513d987b519f0ecd732e7031241c50328/bitnami.
|
POSTGRES_CHART_VERSION
| Helm Chart version used for PostgreSQL chart. Defaults to 8.2.1.
|
Job-disabling variables
Use these variables to disable CI/CD jobs.
| Job name | CI/CD variable | GitLab version | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
.fuzz_base
| COVFUZZ_DISABLED
| From GitLab 13.2 |
Read more about how .fuzz_base provide capability for your own jobs. If the variable is present, your jobs aren’t created.
|
apifuzzer_fuzz
| API_FUZZING_DISABLED
| From GitLab 13.3 | If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. |
build
| BUILD_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
build_artifact
| BUILD_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
bandit-sast
| SAST_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
brakeman-sast
| SAST_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
canary
| CANARY_ENABLED
| This manual job is created if the variable is present. | |
cluster_image_scanning
| CLUSTER_IMAGE_SCANNING_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
code_intelligence
| CODE_INTELLIGENCE_DISABLED
| From GitLab 13.6 | If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. |
code_quality
| CODE_QUALITY_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
container_scanning
| CONTAINER_SCANNING_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
dast
| DAST_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
dast_environment_deploy
|
DAST_DISABLED_FOR_DEFAULT_BRANCH or DAST_DISABLED
| From GitLab 12.4 | If either variable is present, the job isn’t created. |
dependency_scanning
| DEPENDENCY_SCANNING_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
eslint-sast
| SAST_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
flawfinder-sast
| SAST_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
gemnasium-dependency_scanning
| DEPENDENCY_SCANNING_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
gemnasium-maven-dependency_scanning
| DEPENDENCY_SCANNING_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
gemnasium-python-dependency_scanning
| DEPENDENCY_SCANNING_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
gosec-sast
| SAST_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
kubesec-sast
| SAST_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
license_management
| LICENSE_MANAGEMENT_DISABLED
| GitLab 12.7 and earlier | If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. Job deprecated from GitLab 12.8 |
license_scanning
| LICENSE_MANAGEMENT_DISABLED
| From GitLab 12.8 | If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. |
load_performance
| LOAD_PERFORMANCE_DISABLED
| From GitLab 13.2 | If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. |
nodejs-scan-sast
| SAST_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
performance
| PERFORMANCE_DISABLED
| GitLab 13.12 and earlier | Browser performance. If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. Replaced by browser_performance.
|
browser_performance
| BROWSER_PERFORMANCE_DISABLED
| From GitLab 14.0 | Browser performance. If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. Replaces performance.
|
phpcs-security-audit-sast
| SAST_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
pmd-apex-sast
| SAST_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
review
| REVIEW_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
review:stop
| REVIEW_DISABLED
| Manual job. If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
sast
| SAST_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
sast:container
| CONTAINER_SCANNING_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
secret_detection
| SECRET_DETECTION_DISABLED
| From GitLab 13.1 | If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. |
secret_detection_default_branch
| SECRET_DETECTION_DISABLED
| From GitLab 13.2 | If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. |
security-code-scan-sast
| SAST_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
secrets-sast
| SAST_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
sobelaw-sast
| SAST_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
stop_dast_environment
|
DAST_DISABLED_FOR_DEFAULT_BRANCH or DAST_DISABLED
| From GitLab 12.4 | If either variable is present, the job isn’t created. |
spotbugs-sast
| SAST_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
test
| TEST_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
staging
| STAGING_ENABLED
| The job is created if the variable is present. | |
stop_review
| REVIEW_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. |
Configure application secret variables
Some deployed applications require access to secret variables.
Auto DevOps detects CI/CD variables starting with K8S_SECRET_,
and makes them available to the deployed application as
environment variables.
Prerequisite:
- The variable value must be a single line.
To configure secret variables:
- On the top bar, select Main menu > Projects and find your project.
- On the left sidebar, select Settings > CI/CD.
- Expand Variables.
- Create a CI/CD variable with the prefix
K8S_SECRET_. For example, you can create a variable calledK8S_SECRET_RAILS_MASTER_KEY. - Run an Auto DevOps pipeline, either by manually creating a new pipeline or by pushing a code change to GitLab.
Kubernetes secrets
Auto DevOps pipelines use your application secret variables to
populate a Kubernetes secret. This secret is unique per environment.
When deploying your application, the secret is loaded as environment
variables in the container running the application. For example, if
you create a secret called K8S_SECRET_RAILS_MASTER_KEY, your
Kubernetes secret might look like:
$ kubectl get secret production-secret -n minimal-ruby-app-54 -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
data:
RAILS_MASTER_KEY: MTIzNC10ZXN0
kind: Secret
metadata:
creationTimestamp: 2018-12-20T01:48:26Z
name: production-secret
namespace: minimal-ruby-app-54
resourceVersion: "429422"
selfLink: /api/v1/namespaces/minimal-ruby-app-54/secrets/production-secret
uid: 57ac2bfd-03f9-11e9-b812-42010a9400e4
type: Opaque
Update application secrets
Environment variables are generally immutable in a Kubernetes pod. If you update an application secret and then manually create a new pipeline, running applications do not receive the updated secret.
To update application secrets, either:
- Push a code update to GitLab to force the Kubernetes deployment to recreate pods.
- Manually delete running pods to cause Kubernetes to create new pods with updated secrets.
Variables with multi-line values are not supported due to limitations with the Auto DevOps scripting environment.
Configure replica variables
Add replica variables when you want to scale your deployments:
- Add a replica variable as a project CI/CD variable.
-
To scale your application, redeploy it.
Do not scale your application using Kubernetes directly. Helm might not detect the change, and subsequent deployments with Auto DevOps can undo your changes.
Custom replica variables
You can create custom replica variables with the format <TRACK>_<ENV>_REPLICAS:
-
<TRACK>is the all-caps value of thetrackKubernetes label set in the Helm Chart app definition. Iftrackis not set, omit<TRACK>from the custom variable. -
<ENV>is the all-caps environment name of the deploy job set in.gitlab-ci.yml.
For example, if the environment is qa and the track is
foo, create an environment variable called FOO_QA_REPLICAS:
QA testing:
stage: deploy
environment:
name: qa
script:
- deploy foo
The track foo must be defined in the application’s Helm chart.
For example:
replicaCount: 1
image:
repository: gitlab.example.com/group/project
tag: stable
pullPolicy: Always
secrets:
- name: gitlab-registry
application:
track: foo
tier: web
service:
enabled: true
name: web
type: ClusterIP
url: http://my.host.com/
externalPort: 5000
internalPort: 5000
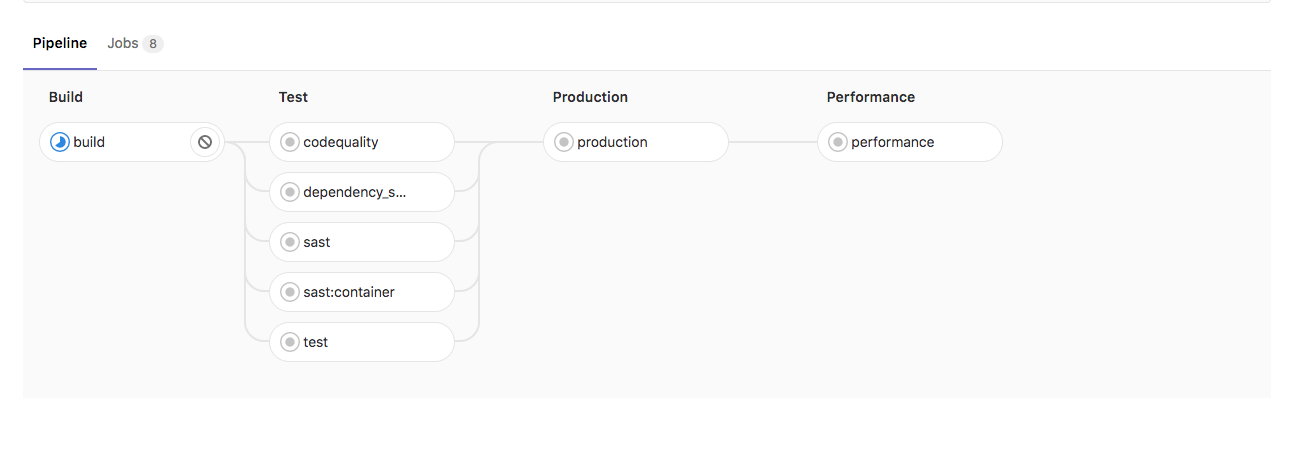
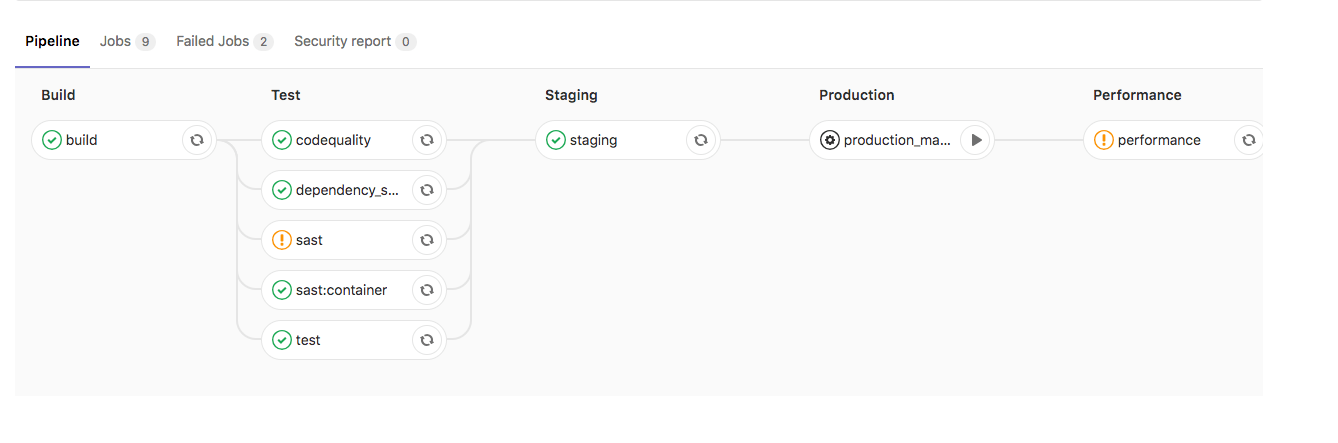
Deploy policy for staging and production environments
Auto DevOps typically uses continuous deployment, and pushes
automatically to the production environment whenever a new pipeline
runs on the default branch. To deploy to production manually, you can
use the STAGING_ENABLED CI/CD variable.
If you set STAGING_ENABLED, GitLab automatically deploys the
application to a staging environment. When you’re ready to deploy to
production, GitLab creates a production_manual job.
You can also enable manual deployment in your project settings.
Deploy policy for canary environments
You can use a canary environment before deploying any changes to production.
If you set CANARY_ENABLED, GitLab creates two manual jobs:
-
canary- Deploys the application to the canary environment. -
production_manual- Deploys the application to production.
Incremental rollout to production
Use an incremental rollout to continuously deploy your application, starting with only a few pods. You can increase the number of pods manually.
You can enable manual deployment in your project settings,
or by setting INCREMENTAL_ROLLOUT_MODE to manual.
If you set INCREMENTAL_ROLLOUT_MODE to manual, GitLab creates four
manual jobs:
rollout 10%rollout 25%rollout 50%rollout 100%
The percentage is based on the REPLICAS CI/CD variable, and defines the number of
pods used for deployment. For example, if the value is 10 and you run the
10% rollout job, your application is deployed to only one pod.
You can run the rollout jobs in any order. To scale down, rerun a lower percentage job.
After you run the rollout 100% job, you cannot scale down, and must
roll back your deployment.
Example incremental rollout configurations
Without INCREMENTAL_ROLLOUT_MODE and without STAGING_ENABLED:
Without INCREMENTAL_ROLLOUT_MODE and with STAGING_ENABLED:
With INCREMENTAL_ROLLOUT_MODE set to manual and without STAGING_ENABLED:
With INCREMENTAL_ROLLOUT_MODE set to manual and with STAGING_ENABLED:
Timed incremental rollout to production
Use a timed incremental rollout to continuously deploy your application, starting with only a few pods.
You can enable timed incremental deployment in your project settings,
or by setting the INCREMENTAL_ROLLOUT_MODE CI/CD variable to timed.
If you set INCREMENTAL_ROLLOUT_MODE to timed, GitLab creates four jobs:
timed rollout 10%timed rollout 25%timed rollout 50%timed rollout 100%
There is a five-minute delay between jobs.