- Features per tier
- View Code Quality results
- Enable Code Quality
- Disable Code Quality
- Customizing scan settings
- Output
- Use Code Quality with merge request pipelines
- Use a private container image registry
- Use DockerHub with authentication
- Use the Dependency Proxy
- Implement a custom tool
- Using Analysis Plugins
-
Troubleshooting
- Changing the default configuration has no effect
- No Code Quality report is displayed in a merge request
- Only a single Code Quality report is displayed, but more are defined
- RuboCop errors
- No Code Quality appears on merge requests when using custom tool
- Error:
Could not analyze code quality - Using Code Quality with Kubernetes CI executor
-
Error:
x509: certificate signed by unknown authority
Code Quality
Moved to GitLab Free in 13.2.
Use Code Quality to analyze your source code’s quality and complexity. This helps keep your project’s code simple, readable, and easier to maintain. Code Quality should supplement your other review processes, not replace them.
Code Quality uses the open source Code Climate tool, and selected plugins, to analyze your source code. To confirm if your code’s languages are covered, see the Code Climate list of Supported Languages for Maintainability. You can extend the code coverage either by using Code Climate Analysis Plugins or a custom tool.
Run Code Quality reports in your CI/CD pipeline to verify changes don’t degrade your code’s quality, before committing them to the default branch.
Features per tier
Different features are available in different GitLab tiers, as shown in the following table:
| Capability | In Free | In Premium | In Ultimate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Configure scanners | |||
| Integrate custom scanners | |||
| See findings in merge request widget | |||
| Generate JSON or HTML report artifacts | |||
| See reports in CI pipelines | |||
| See findings in merge request diff view |
View Code Quality results
Code Quality results are shown in the:
- Merge request widget
- Merge request changes view
- Pipeline details view
Merge request widget
Moved to GitLab Free in 13.2.
Code Quality analysis results display in the merge request widget area if a report from the target branch is available for comparison.
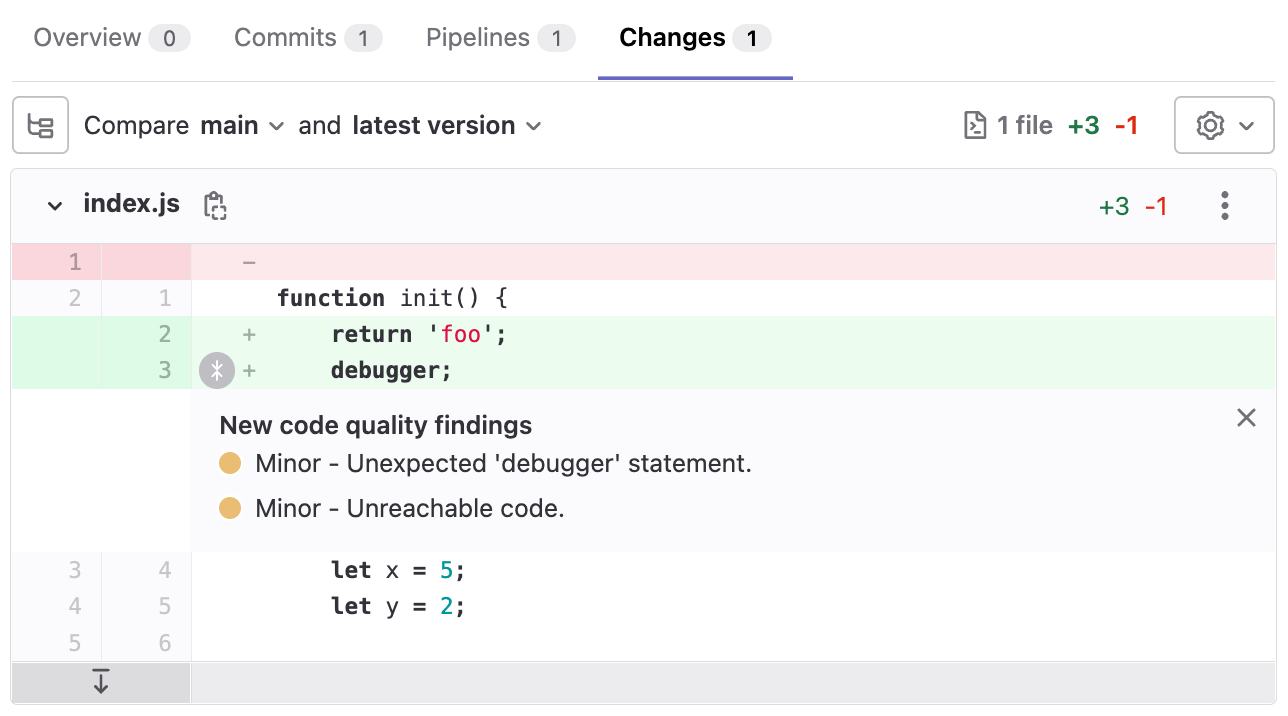
Merge request changes view
-
Introduced in GitLab 13.11, disabled by default behind the
codequality_mr_difffeature flag. - Enabled by default in GitLab 13.12.
- Disabled by default in GitLab 14.0 due to this issue.
- Inline annotation added and feature flag removed in GitLab 14.1.
Code Quality results display in the merge request Changes view. Lines containing Code Quality issues are marked by an indicator beside the gutter. Hover over the marker for details of the issue.
Pipeline details view
The full list of Code Quality violations generated by a pipeline is shown in the Code Quality tab of the pipeline’s details page.
Enable Code Quality
Prerequisites:
- GitLab CI/CD configuration (
.gitlab-ci.yml) must include theteststage. - If you’re using shared runners, the Code Quality job must be configured for the Docker-in-Docker workflow.
- If you’re using private runners, you should use an alternative configuration recommended for running Code Quality analysis more efficiently.
- The runner must have enough disk space to store the generated Code Quality files. For example, on the GitLab project the files are approximately 7 GB.
To enable Code Quality, either:
-
Enable Auto DevOps, which includes Auto Code Quality.
-
Include the Code Quality template in your
.gitlab-ci.ymlfile.Example:
include: - template: Code-Quality.gitlab-ci.ymlCode Quality now runs in pipelines.
Improve Code Quality performance with private runners
If you have private runners, you should use this configuration for improved performance of Code Quality because:
- Privileged mode is not used.
- Docker-in-Docker is not used.
- Docker images, including all CodeClimate images, are cached, and not re-fetched for subsequent jobs.
This alternative configuration uses socket binding to share the Runner’s Docker daemon with the job environment. Before implementing this configuration, consider its limitations.
To use private runners:
-
Register a new runner:
$ gitlab-runner register --executor "docker" \ --docker-image="docker:stable" \ --url "https://gitlab.com/" \ --description "cq-sans-dind" \ --tag-list "cq-sans-dind" \ --locked="false" \ --access-level="not_protected" \ --docker-volumes "/cache"\ --docker-volumes "/builds:/builds"\ --docker-volumes "/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock" \ --registration-token="<project_token>" \ --non-interactive -
Optional, but recommended: Set the builds directory to
/tmp/builds, so job artifacts are periodically purged from the runner host. If you skip this step, you must clean up the default builds directory (/builds) yourself. You can do this by adding the following two flags togitlab-runner registerin the previous step.--builds-dir "/tmp/builds" --docker-volumes "/tmp/builds:/tmp/builds" # Use this instead of --docker-volumes "/builds:/builds"The resulting configuration:
[[runners]] name = "cq-sans-dind" url = "https://gitlab.com/" token = "<project_token>" executor = "docker" builds_dir = "/tmp/builds" [runners.docker] tls_verify = false image = "docker:stable" privileged = false disable_entrypoint_overwrite = false oom_kill_disable = false disable_cache = false volumes = ["/cache", "/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock", "/tmp/builds:/tmp/builds"] shm_size = 0 [runners.cache] [runners.cache.s3] [runners.cache.gcs] -
Apply two overrides to the
code_qualityjob created by the template:include: - template: Code-Quality.gitlab-ci.yml code_quality: services: # Shut off Docker-in-Docker tags: - cq-sans-dind # Set this job to only run on our new specialized runner
Code Quality now runs in standard Docker mode.
Disable Code Quality
The code_quality job doesn’t run if the $CODE_QUALITY_DISABLED CI/CD variable
is present. Refer to the CI/CD variables documentation
to learn more about how to define one.
To disable Code Quality, create a custom CI/CD variable named CODE_QUALITY_DISABLED, for either:
Customizing scan settings
The Code Quality scan settings can be changed using CI/CD variables
in .gitlab-ci.yml.
To configure the Code Quality job:
- Declare a job with the same name as the Code Quality job, after the template’s inclusion.
- Specify additional keys in the job’s stanza.
For an example, see Download output in JSON format.
Available CI/CD variables
In GitLab 13.4 and later, the option to override the Code Quality environment variables was added.
Code Quality can be customized by defining available CI/CD variables:
| CI/CD variable | Description |
|---|---|
SOURCE_CODE
| Path to the source code to scan. |
TIMEOUT_SECONDS
| Custom timeout for the codeclimate analyze command.
|
CODECLIMATE_DEBUG
| Set to enable Code Climate debug mode |
CODECLIMATE_DEV
| Set to enable --dev mode which lets you run engines not known to the CLI.
|
REPORT_STDOUT
| Set to print the report to STDOUT instead of generating the usual report file.
|
REPORT_FORMAT
| Set to control the format of the generated report file. One of: json\|html.
|
ENGINE_MEMORY_LIMIT_BYTES
| Set the memory limit for engines, default is 1,024,000,000 bytes. |
CODE_QUALITY_DISABLED
| Prevents the Code Quality job from running. |
CODECLIMATE_PREFIX
| Set a prefix to use with all docker pull commands in CodeClimate engines. Useful for offline scanning.
|
Output
Code Quality creates a file named gl-code-quality-report.json. The content of this file is
processed internally and the results shown in the UI. To see the raw results, you can
configure the Code Quality job to allow download of this file. Format options are JSON format, HTML
format, or both. Use the HTML format to view the report in a more human-readable
format. For example, you could publish the HTML format file on GitLab Pages for even easier
reviewing.
Download output in JSON format
To be able to download the Code Quality report in JSON format, declare the
gl-code-quality-report.json file as an artifact of the code_quality job:
include:
- template: Code-Quality.gitlab-ci.yml
code_quality:
artifacts:
paths: [gl-code-quality-report.json]
The full JSON file is available as a
downloadable artifact of the code_quality
job.
Download output in JSON and HTML format
HTML report format introduced in GitLab 13.6.
To be able to download the Code Quality report in both JSON and HTML format, add another job to your
template by using extends: code_quality:
include:
- template: Code-Quality.gitlab-ci.yml
code_quality_html:
extends: code_quality
variables:
REPORT_FORMAT: html
artifacts:
paths: [gl-code-quality-report.html]
Both the JSON and HTML files are available as
downloadable artifacts of the code_quality
job.
Download output in only HTML format
To download the Code Quality report in only an HTML format file, set REPORT_FORMAT to html in
the existing job.
include:
- template: Code-Quality.gitlab-ci.yml
code_quality:
variables:
REPORT_FORMAT: html
artifacts:
paths: [gl-code-quality-report.html]
The HTML file is available as a
downloadable artifact of the code_quality
job.
Use Code Quality with merge request pipelines
The default Code Quality configuration does not allow the code_quality job to run on
merge request pipelines.
To enable Code Quality to run on merge request pipelines, overwrite the code quality rules,
or workflow: rules, so that they match your current rules.
For example:
include:
- template: Code-Quality.gitlab-ci.yml
code_quality:
rules:
- if: $CODE_QUALITY_DISABLED
when: never
- if: $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "merge_request_event" # Run code quality job in merge request pipelines
- if: $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == $CI_DEFAULT_BRANCH # Run code quality job in pipelines on the default branch (but not in other branch pipelines)
- if: $CI_COMMIT_TAG # Run code quality job in pipelines for tags
Use a private container image registry
Introduced in GitLab 13.7.
Using a private container image registry can reduce the time taken to download images, and also
reduce external dependencies. Because of the nested architecture of container execution, the
registry prefix must be specifically configured to be passed down into CodeClimate’s subsequent
docker pull commands for individual engines.
The following variables can address all of the required image pulls:
-
CODE_QUALITY_IMAGE: A fully prefixed image name that can be located anywhere accessible from your job environment. GitLab Container Registry can be used here to host your own copy. -
CODECLIMATE_PREFIX: The domain of your intended container image registry. This is a configuration option supported by CodeClimate CLI. You must:- Include a trailing slash (
/). - Not include a protocol prefix, such as
https://.
- Include a trailing slash (
-
CODECLIMATE_REGISTRY_USERNAME: An optional variable to specify the username for the registry domain parsed fromCODECLIMATE_PREFIX. -
CODECLIMATE_REGISTRY_PASSWORD: An optional variable to specify the password for the registry domain parsed fromCODECLIMATE_PREFIX.
include:
- template: Code-Quality.gitlab-ci.yml
code_quality:
variables:
CODE_QUALITY_IMAGE: "my-private-registry.local:12345/codequality:0.85.24"
CODECLIMATE_PREFIX: "my-private-registry.local:12345/"
This example is specific to GitLab Code Quality. For more general instructions on how to configure DinD with a registry mirror, see Enable registry mirror for Docker-in-Docker service.
Required images
The following images are required for the default .codeclimate.yml:
codeclimate/codeclimate-structure:latestcodeclimate/codeclimate-csslint:latestcodeclimate/codeclimate-coffeelint:latestcodeclimate/codeclimate-duplication:latestcodeclimate/codeclimate-eslint:latestcodeclimate/codeclimate-fixme:latestcodeclimate/codeclimate-rubocop:rubocop-0-92
If you are using a custom .codeclimate.yml configuration file, you must add the specified plugins in your private container registry.
Use DockerHub with authentication
You can use DockerHub as an alternate source of the Code Quality images.
Prerequisites:
- Add the username and password as protected CI/CD variables in the project.
To use DockerHub, configure the following variables in the .gitlab-ci.yml file:
CODECLIMATE_PREFIXCODECLIMATE_REGISTRY_USERNAMECODECLIMATE_REGISTRY_PASSWORD
Example:
include:
- template: Jobs/Code-Quality.gitlab-ci.yml
code_quality:
variables:
CODECLIMATE_PREFIX: "registry-1.docker.io/"
CODECLIMATE_REGISTRY_USERNAME: $DOCKERHUB_USERNAME
CODECLIMATE_REGISTRY_PASSWORD: $DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD
Use the Dependency Proxy
You can use a Dependency Proxy to reduce the time taken to download dependencies.
Prerequisite:
- Dependency Proxy enabled in the project’s group.
To reference the Dependency Proxy, configure the following variables in the .gitlab-ci.yml file:
CODE_QUALITY_IMAGECODECLIMATE_PREFIXCODECLIMATE_REGISTRY_USERNAMECODECLIMATE_REGISTRY_PASSWORD
For example:
include:
- template: Code-Quality.gitlab-ci.yml
code_quality:
variables:
CODE_QUALITY_IMAGE: "$CI_DEPENDENCY_PROXY_GROUP_IMAGE_PREFIX/codequality:0.85.24"
## You must add a trailing slash to `$CI_DEPENDENCY_PROXY_GROUP_IMAGE_PREFIX`.
CODECLIMATE_PREFIX: $CI_DEPENDENCY_PROXY_GROUP_IMAGE_PREFIX/
CODECLIMATE_REGISTRY_USERNAME: $CI_DEPENDENCY_PROXY_USER
CODECLIMATE_REGISTRY_PASSWORD: $CI_DEPENDENCY_PROXY_PASSWORD
Implement a custom tool
You can integrate a custom tool into GitLab to provide Code Quality reports.
The Code Quality report artifact JSON file must contain an array of objects with the following properties:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
description
| A description of the code quality violation. |
fingerprint
| A unique fingerprint to identify the code quality violation. For example, an MD5 hash. |
severity
| A severity string (can be info, minor, major, critical, or blocker).
|
location.path
| The relative path to the file containing the code quality violation. |
location.lines.begin or location.positions.begin.line
| The line on which the code quality violation occurred. |
To implement a custom Code Quality tool:
- Define a job in your
.gitlab-ci.ymlfile that generates the Code Quality report artifact. - Configure the tool to generate the Code Quality report artifact as a JSON file that implements a subset of the Code Climate spec.
Example:
[
{
"description": "'unused' is assigned a value but never used.",
"fingerprint": "7815696ecbf1c96e6894b779456d330e",
"severity": "minor",
"location": {
"path": "lib/index.js",
"lines": {
"begin": 42
}
}
}
]
Using Analysis Plugins
Code Quality functionality can be extended by using Code Climate Analysis Plugins.
For example, to use the SonarJava analyzer:
- Add a file named
.codeclimate.ymlto the root of your repository - Add to the
.codeclimate.ymlthe enablement code for the plugin to the root of your repository:
version: "2"
plugins:
sonar-java:
enabled: true
This adds SonarJava to the plugins: section of the
default .codeclimate.yml
included in your project.
Changes to the plugins: section do not affect the exclude_patterns section of the default
.codeclimate.yml. See the Code Climate documentation on
excluding files and folders
for more details.
Troubleshooting
Changing the default configuration has no effect
A common issue is that the terms Code Quality (GitLab specific) and Code Climate
(Engine used by GitLab) are very similar. You must add a .codeclimate.yml file
to change the default configuration, not a .codequality.yml file. If you use
the wrong filename, the default .codeclimate.yml
is still used.
No Code Quality report is displayed in a merge request
This can be due to multiple reasons:
- You just added the Code Quality job in your
.gitlab-ci.yml. The report does not have anything to compare to yet, so no information can be displayed. It only displays after future merge requests have something to compare to. - Your pipeline is not set to run the code quality job on your target branch. If there is no report
generated from the target branch, your merge request branch reports have nothing to compare to. In this
situation you get an error stating
Base pipeline codequality artifact not found. - The
artifacts:expire_inCI/CD setting can cause the Code Quality artifacts to expire faster than desired. - The widgets use the pipeline of the latest commit to the target branch. If commits are made to the default branch that do not run the code quality job, this may cause the merge request widget to have no base report for comparison.
- If you use the
REPORT_STDOUTenvironment variable, no report file is generated and nothing displays in the merge request.
Only a single Code Quality report is displayed, but more are defined
Starting in GitLab 15.7, Code Quality combines the results from all jobs in a pipeline.
In previous versions, GitLab only uses the Code Quality artifact from the latest created job (with the largest job ID). If multiple jobs in a pipeline generate a code quality artifact, those of earlier jobs are ignored.
To avoid confusion, configure only one job to generate a gl-code-quality-report.json file.
RuboCop errors
When using Code Quality jobs on a Ruby project, you can encounter problems running RuboCop. For example, the following error can appear when using either a very recent or very old version of Ruby:
/usr/local/bundle/gems/rubocop-0.52.1/lib/rubocop/config.rb:510:in `check_target_ruby':
Unknown Ruby version 2.7 found in `.ruby-version`. (RuboCop::ValidationError)
Supported versions: 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4, 2.5
This is caused by the default version of RuboCop used by the check engine not covering support for the Ruby version in use.
To use a custom version of RuboCop that
supports the version of Ruby used by the project,
you can override the configuration through a .codeclimate.yml file
created in the project repository.
For example, to specify using RuboCop release 0.67:
version: "2"
plugins:
rubocop:
enabled: true
channel: rubocop-0-67
No Code Quality appears on merge requests when using custom tool
If your merge requests do not show any Code Quality changes when using a custom tool, ensure that
the line property is an integer.
Error: Could not analyze code quality
You might get the error:
error: (CC::CLI::Analyze::EngineFailure) engine pmd ran for 900 seconds and was killed
Could not analyze code quality for the repository at /code
If you enabled any of the Code Climate plugins, and the Code Quality CI/CD job fails with this error message, it’s likely the job takes longer than the default timeout of 900 seconds:
To work around this problem, set TIMEOUT_SECONDS to a higher value in your .gitlab.-ci.yml file.
For example:
variables:
TIMEOUT_SECONDS: 3600
Using Code Quality with Kubernetes CI executor
Code Quality requires a Docker in Docker setup to work. The Kubernetes executor already has support for this.
To ensure Code Quality jobs can run on a Kubernetes executor:
- If you’re using TLS to communicate with the Docker daemon, the executor must be running in privileged mode. Additionally, the certificate directory must be specified as a volume mount.
- It is possible that the DinD service doesn’t start up fully before the Code Quality job starts. This is a limitation documented in the Kubernetes executor for GitLab Runner troubleshooting section.
Error: x509: certificate signed by unknown authority
If you set the CODE_QUALITY_IMAGE to an image that is hosted in a Docker registry which uses a TLS
certificate that is not trusted, such as a self-signed certificate, you can see errors like the one
below:
$ docker pull --quiet "$CODE_QUALITY_IMAGE"
Error response from daemon: Get https://gitlab.example.com/v2/: x509: certificate signed by unknown authority
To fix this, configure the Docker daemon to trust certificates
by putting the certificate inside of the /etc/docker/certs.d directory.
This Docker daemon is exposed to the subsequent Code Quality Docker container in the GitLab Code Quality template and should be to exposed any other containers in which you want to have your certificate configuration apply.
Docker
If you have access to GitLab Runner configuration, add the directory as a volume mount.
Replace gitlab.example.com with the actual domain of the registry.
Example:
[[runners]]
...
executor = "docker"
[runners.docker]
...
privileged = true
volumes = ["/cache", "/etc/gitlab-runner/certs/gitlab.example.com.crt:/etc/docker/certs.d/gitlab.example.com/ca.crt:ro"]
Kubernetes
If you have access to GitLab Runner configuration and the Kubernetes cluster, you can mount a ConfigMap.
Replace gitlab.example.com with the actual domain of the registry.
-
Create a ConfigMap with the certificate:
kubectl create configmap registry-crt --namespace gitlab-runner --from-file /etc/gitlab-runner/certs/gitlab.example.com.crt -
Update GitLab Runner
config.tomlto specify the ConfigMap:[[runners]] ... executor = "kubernetes" [runners.kubernetes] image = "alpine:3.12" privileged = true [[runners.kubernetes.volumes.config_map]] name = "registry-crt" mount_path = "/etc/docker/certs.d/gitlab.example.com/ca.crt" sub_path = "gitlab.example.com.crt"